这篇 blog 来分析一下 ConcurrentHashMap 的源码。JDK 1.7 和 JDK 1.8 中的 ConcurrentHashMap 区别很大,这里我们分版本来看看
JDK 1.7
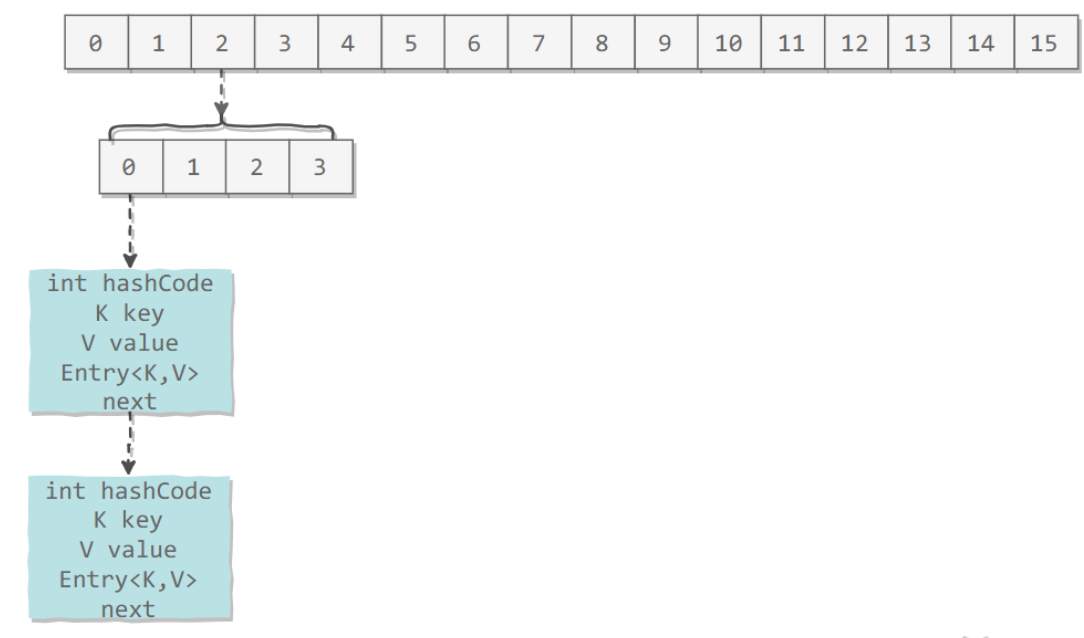
JDK 1.7 使用分段锁机制来实现并发更新操作,核心类为 Segment,它继承自重入锁 ReentrantLock,并发度与 Segment 数量相等
static final class HashEntry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V value;
volatile HashEntry<K,V> next;
}
ConcurrentHashMap 和 HashMap 实现上类似,最主要的差别是 ConcurrentHashMap 采用了分段锁(Segment),每个分段锁维护着几个桶(HashEntry),多个线程可以同时访问不同分段锁上的桶,从而使其并发度更高(并发度就是 Segment 的个数)
Segment 继承自 ReentrantLock
static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2249069246763182397L;
static final int MAX_SCAN_RETRIES =
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() > 1 ? 64 : 1;
transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table;
transient int count;
transient int modCount;
transient int threshold;
final float loadFactor;
}
final Segment<K,V>[] segments;
默认的并发级别为 16,也就是说默认创建 16 个 Segment
static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;
JDK 1.8
JDK 1.8 中使用了 CAS 操作和内置锁 synchronized 来支持更高的并发度
Node 类
ConcurrentHashMap 的 Node 类和 HashMap 有所不同,val 和 next 字段都用 volatile 修饰了
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V val;
volatile Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return val; }
public final int hashCode() { return key.hashCode() ^ val.hashCode(); }
public final String toString(){ return key + "=" + val; }
public final V setValue(V value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
Object k, v, u; Map.Entry<?,?> e;
return ((o instanceof Map.Entry) &&
(k = (e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o).getKey()) != null &&
(v = e.getValue()) != null &&
(k == key || k.equals(key)) &&
(v == (u = val) || v.equals(u)));
}
Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) {
Node<K,V> e = this;
if (k != null) {
do {
K ek;
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
return null;
}
}
get 方法
ConcurrentHashMap 的 get 方法和 HashMap 类似,同样是使用除留余数法获取 key 在 table 中的下标,沿着链表或红黑树寻找,这里没有加锁,因为 Node 类的 val 和 next 都用 volatile 修饰了,当字段更改的时候,线程会立马知道
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
put 方法
ConcurrentHashMap 的 put 方法和 HashMap 中类似,我们来看看不同的地方
- ConcurrentHashMap 的 key 和 value 都不能为 null,否则 putVal 方法会抛出 NullPointerException
- ConcurrentHashMap 通过除留余数法获取 key 位于 table 数组的下标,然后使用 synchronized 对 table[idx] 的 Node 实例加锁,也就是锁根节点
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
扩容
JDK 1.8 中,采用多线程扩容。整个扩容过程,通过 CAS 设置 sizeCtl,transferIndex 等变量协调多个线程进行并发扩容